Atrial Flutter
Atrial Flutter (A-Flutter) is an abnormal fluttering heart rhythm that occurs in the atria portion of the heart. A-Flutter is generally characterized with a rapid increase in the patient heart rate over 100 Beats per minute (tachycardia)n classified as Supraventricular Tachycardia. A Flutter occurs most often in patients that have documented cardiovascular disease such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy as well as diabetes. However, A Flutter can be known to happen in patient with no diagnosed heart problems. Atrial Flutter is not a stable rhythm, and can frequently turn into Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib). Atrial Flutter rarely persist for for periods of a few months lasting up to multiple years.
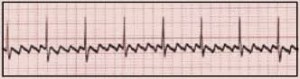 A Flutter is generally an unstable cardiac rhythm described by rapid P waves or fluttering waves with varying blocks at the AV Node of the heart. Atrial heart rates can be as high as 220-350 with non-consistent ventricular responses varying from 1 to 1 or up to 1 and 5 ventricular response to each atrial action. This ration is known to determine the patient’s heart rate. Atrial Flutter waves typically appear in a sawtooth pattern making it distinct in ECG waveform morphology.
A Flutter is generally an unstable cardiac rhythm described by rapid P waves or fluttering waves with varying blocks at the AV Node of the heart. Atrial heart rates can be as high as 220-350 with non-consistent ventricular responses varying from 1 to 1 or up to 1 and 5 ventricular response to each atrial action. This ration is known to determine the patient’s heart rate. Atrial Flutter waves typically appear in a sawtooth pattern making it distinct in ECG waveform morphology.
Atrial Flutter can be dangerous if not managed properly. Much like Atrial Fibrillation, A-Flutter is an unstable rhythm condition that can lead to heart attack or stroke.




